
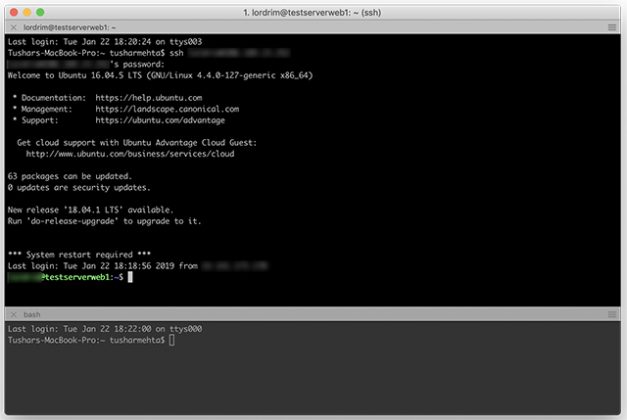
The terminal then shows something similar to: logoutĪt this point, the shell prompt returns to the one for the local workstation and the terminal application can be closed if it’s no longer needed. Ending the SSH SessionĪfter you are done, log out of the session by typing exit. Getting to know these commands will help you navigate around your server. This includes many of the basic Linux commands, such as ls, cd, rm, and those covered in Using the Terminal guide. You can now run any commands that you have available on that server. Your command prompt should now show the username and hostname configured for the server. Once you have successfully connected, your terminal should be using the remote shell environment for the server.
ssh-keygen -R 198.51.100.4Īccept the prompt by entering y or yes, which results in a one-time warning that is similar to: Warning: Permanently added 'example' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. To fix this, revoke the key for that IP address. This happens when remote host key changes. If you recently rebuilt your server, you might receive an error message when you try to connect. Refer to Apple’s Open or Quit Terminal on Mac guide for additional methods of opening Terminal. In the search results, click on Terminal.app. To open this program, access Spotlight by pressing Cmd + Space on the keyboard and type “Terminal” in the search box.

The default terminal emulator for macOS is called Terminal. The terminal allows you to access your operating system’s shell environment and run programs through the command line. On your local computer, open the terminal application you wish to use. If you wish to deploy a new server, follow the Creating a Compute Instance guide to create a Linode. Most Linux distributions have an SSH server preinstalled. Before You BeginĮnsure you have a Linux server with an SSH server (like OpenSSH) installed. This article covers the basics of connecting to a remote server (such as a Linode) over SSH on macOS. When most people refer to SSH, it is within the context of a connecting from a local computer to a remote server, commonly for administration tasks related to website hosting. A secure shell (SSH) is used for secure communication between devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
